tredmond@sfbg.com, steve@sfbg.com
The most important political change of 2012 may not be the appointment of a new District 5 supervisor or the inauguration of a new mayor and sheriff. A process moving slowly through a little-known city task force could wind up profoundly shifting the makeup, and balance of power, on the Board of Supervisors — and hardly anyone is paying attention, yet.
The Redistricting Task Force is in the process of drawing new lines for the supervisorial districts, as mandated every 10 years when new census data is available. The nine-member body is made up of three appointees each by the board, the mayor and the Elections Commission. While mandated to draw equal-sized districts that maintain “communities of interest,” the board has almost unchecked authority to decide which voters are in which districts.
While it’s difficult to draw 11 bad districts in San Francisco, it’s entirely possible to shift the lines to make it more difficult to elect progressives — something many groups out there are anxious to do.
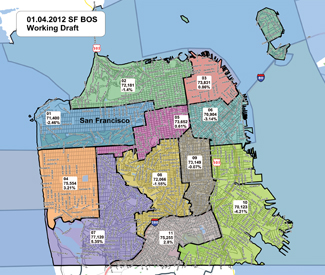
VIEW THE CURRENT WORKING DRAFT MAP HERE
CONSOLIDATING THE LEFT
Downtown and pro-landlord groups are circulating their own draft maps, attempting to influence the outcome. Their goal is hardly a secret: If progressive voters can be concentrated in a small number of districts — say, districts 5, 6, and 9 — it’s more likely that a majority of the board will be moderates and conservatives.
The task force has looked at 10 “visualizations” prepared by a consultant, and each of them had some alarming aspects. For example, the visualizations mostly pushed such conservative areas as Seacliff and Presidio Heights into District 1, which is represented by progressive Sup. Eric Mar.
On Jan. 4, those drafts were replaced by a single working draft map, which is now on the task force’s hard-to-find website (www.sfgov2.org/index.aspx?page=2622) — and it’s not as bad as the earlier versions. The working draft keeps Seacliff and Presidio Terrace in District 2 — which share similar demographics.
“The working families in the Richmond don’t belong in the same community of interest as the millionaires with homes overlooking the ocean,” Mar told us.
But there are other changes that some may find alarming. The more conservative Portola neighborhood, which is now in District 9, would be included in District 11, while D9 would pick up the more liberal north Mission. That would make D9 an even safer progressive district — but make D11 harder for a progressive like the incumbent, John Avalos, to win.
The task force has been holding hearings on each of the districts — but there’s been little discussion about how the new lines will affect the makeup of the board, and the politics and policy of the city, as a whole.
POPULATION CHANGES
The driving force behind the changes in the districts is the rather dramatic population shift on the east side of the city. Most of the districts, census data show, have been relatively stable. But since 2000, 24,591 more people have moved into D6 — a nearly 30 percent increase — while 5,465 have moved into D10 (a 7.5 percent increase) and 5,414 into D11 (8.7 percent). D9 saw the biggest population decrease, losing 7,530 voters or 10.3 percent.
The huge growth in D6 has been the result of a boom in new high-end condos in the Rincon Hill and SoMa neighborhoods, and it’s changed the demographics of that district and forced the city to rethink how all of the surrounding districts are drawn.
No matter what scenario you look at, D6 has to become geographically smaller. Most of the maps circulating around suggest that the north Mission be shifted into D9 and parts of the Tenderloin move into districts 3 and 5. But those moves will make D6 less progressive, and create a challenge: The residents of the Tenderloin don’t have a lot in common with the millionaires in their high-rise condos.
As progressive political consultant David Looman noted, “The question is, how do you accommodate both the interests and concerns of San Francisco’s oldest and poorest population and San Francisco’s youngest, hippest, and very prosperous population?”
The working map is far from final. By law, the population of every district has to be within 1 percent of the median district population, or up to 5 percent if needed to prevent dividing or diluting the voting power of minority groups and/or keeping established neighborhoods together.
Under the current draft, eight of the 11 districts are out of compliance with the 1 percent standard, and District 7 has 5.35 percent more residents than the mean, so it will need to change. But task force Chair Eric McDonnell told the Guardian that he expects the current map to be adopted with only slight modifications following a series of public meetings over the next couple months.
“The tweaks will be about how we satisfy the population equalization, while trying to satisfy communities of interest,” McDonnell said, noting that this balancing act won’t be easy. “I anticipate everyone will be disappointed at some level.”
OUTSIDE INFLUENCES?
Some progressives have been concerned that downtown groups have been trying to influence the final map, noting that the San Francisco Board of Realtors, downtown-oriented political consultants David Latterman and Chris Bowman, and others have all created and submitted their own maps to the task force.
McDonnell said the task force considered solutions proposed by the various maps, but he said, “We won’t adopt wholesale anyone’s maps, but we think about what problem they were trying to solve.”
For example, some progressive analysts told us that many of the proposals from downtown make D9 more progressive, even though it is already a solidly progressive seat, while making D8 more conservative, whereas now it is still a contestable district even though moderates have held it for the last decade.
“It would be nice to see the Mission in one district, but it makes D8 considerably more conservative, so it’s a balancing act,” said Tom Radulovich, a progressive activist who ran for D8 supervisor in 2002.
Latterman told us he has a hard time believing the final map will be substantially similar to the current draft. “Once that gets circulated to the neighborhoods, I find that hard to believe it won’t change,” he said. “A lot of the deviations are big and they will have to change.”
He said that he approached the process of making a map as a statistician trying to solve a puzzle, and that begins with figuring out what to do with D6. “I fall back on my technician skills more than the political,” Latterman, who teaches political science at the University of San Francisco, said. “It’s a big puzzle.”
Latterman also disputed concerns that he or others have tried to diminish progressive voting power, saying that’s difficult to do without a drastic remaking of the map, something that few people are advocating.
“It’s hard to make major political changes with the other constraints we have to meet,” he said. “Unless you’re willing to scrap everything we have, it’ll be hard to make major political changes.”
Once the task force approves a final map in April, there’s little that can be done to change it. The map will go to both the Elections Commission and the Board of Supervisors, but neither can alter the boundaries.
“We are the final say,” McDonnell said. That is, unless it is challenged with a lawsuit, which is entirely possible given the stakes.